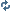|
Thread Rules
1. This is not a "do my homework for me" thread. If you have specific questions, ask, but don't post an assignment or homework problem and expect an exact solution.
2. No recruiting for your cockamamie projects (you won't replace facebook with 3 dudes you found on the internet and $20)
3. If you can't articulate why a language is bad, don't start slinging shit about it. Just remember that nothing is worse than making CSS IE6 compatible.
4. Use [code] tags to format code blocks. |
On December 13 2015 14:49 WarSame wrote:
Right, I get that too. But say you wanted to be able to store 10000 different hash values in the table - do you have to allocate all of them when you first make the table?
There are millions of ways of implementing hash tables (ever heard of perfect hashing?). Generally, you only have an array of pointers/references to your values, so you don't allocate 10000 values at once, you allocate 10000 pointers at once. And if you know that you ultimately will store 10000 values in there, it wouldn't hurt to allocate all these pointers at once. In general, a hash table will start out small though.
Back to the millions of ways - would you expect an interviewee to implement a hash table with guaranteed constant time lookup, insertion and deletion? Amortized constant time? An array of linked lists (or an array of arrays) can't guarantee constant time as far as I know.
|
I would not expect an interviewee to implement a hash table, because it wouldn't show useful signal to the hiring committee. Unless they'd actually never seen a hash table implemented before, it'd be mostly just testing their ability to regurgitate from memory, which isn't interesting. Since you typically are trying to calibrate yourself on a smaller number of questions to maintain consistency between interview candidates, you generally have to opt for more interesting questions that most candidates have likely not seen before.
Right, like I interviewed somewhere around 15-20 candidates this quarter, and used a total of maybe 5 questions. That way I can give a more fair assessment for each candidate. If you don't have a good idea of exactly how hard your question is for a candidate to solve, it's hard to figure out how to score them. It's time consuming to come up with good questions and calibrate yourself on them.
If one of those 5 questions was "implement a hash table" or similar, a good chunk (probably at least half?) would already know how, and I'd have to quickly skip on to another question.
That said, you should be able to talk intelligently about how fast different parts of your algorithms/structures are, what the drawbacks are, etc. You also have to be able to understand how libraries you use perform - if you decide to use a hash table, you should understand what sort of speed you get from different access patterns, how much memory it takes, etc.
|
Hello guys, I have an issue with my multiplayer game in Java.
So it's a turn base board game, I have finished the game logic, I have created a GUI client side, a Server class and a Client class that can connect to the Server. It does multithreading so multiple client can connect, and I can send info to the server.
![[image loading]](http://i.imgur.com/AlJXz2s.png)
As you can see, I can connect, and when I click on a case, it sends coordinate.
Now my issue is : how the heck do I link the game for all of that to works ?
I have the Board class that does all the board modification like flipping pawn, checking valid move etc but I'm lost on this step.
|
On December 14 2015 01:06 Faust852 wrote:Hello guys, I have an issue with my multiplayer game in Java. So it's a turn base board game, I have finished the game logic, I have created a GUI client side, a Server class and a Client class that can connect to the Server. It does multithreading so multiple client can connect, and I can send info to the server. ![[image loading]](http://i.imgur.com/AlJXz2s.png) As you can see, I can connect, and when I click on a case, it sends coordinate. Now my issue is : how the heck do I link the game for all of that to works ? I have the Board class that does all the board modification like flipping pawn, checking valid move etc but I'm lost on this step.
In general, you would choose a main class (Either game, or client, game seemingly makes more sense to my mind right now), then create an instance of the other class (say create an instance of client in game) and use it's api (public methods) to handle communication to the server, while in the main game class.
|
Any Linux users? It's been a while since I last used Linux but I remember using eth0. Now my network interface is called eno1 instead of eth0. Why is this the case? It's a different computer now but what happened to eth0?
|
|
|
The naming scheme with the eth0, eth1, eth2, ... was about the order of the devices being created at boot and later when you hot-plug something or start another driver module.
The new naming scheme has fixed names that are about the spot where things are connected. The system can now do things like start up devices in parallel and no matter which one is faster, the names will stay the same [EDIT: that was probably a stupid thought. I bet it's more about just being able to start up any device that can be found automatically without having any manual configuration and still be able to count on names staying fixed.]
That "eno1" you see is set up by the BIOS of your machine. For me it's "enp6s0", which is perhaps something about the specific PCI-E lane of the chipset it's connected to.
|
On December 14 2015 01:06 Faust852 wrote:Hello guys, I have an issue with my multiplayer game in Java. So it's a turn base board game, I have finished the game logic, I have created a GUI client side, a Server class and a Client class that can connect to the Server. It does multithreading so multiple client can connect, and I can send info to the server. ![[image loading]](http://i.imgur.com/AlJXz2s.png) As you can see, I can connect, and when I click on a case, it sends coordinate. Now my issue is : how the heck do I link the game for all of that to works ? I have the Board class that does all the board modification like flipping pawn, checking valid move etc but I'm lost on this step.
So, from what i understand, you already have clients talking to server, and you already have a class with all game logic done. You can can't do the final step of putting those things together.
First you must decide what kinda of server you have, does the server have all game information, or does it simply transport client calls?
Since it is a board game, and if your task doesn't care about cheating, you server could simply route the messages from one client to another (assuming it is a turn based board game with no time related stuff). Like a chat server. You have all clients with all game logic, your client sends his action to the server and the server routes it to the other client.
If you care about cheating or your game deals with real time stuff, you must have all game logic on server.
|
On December 14 2015 04:58 TMG26 wrote:Show nested quote +On December 14 2015 01:06 Faust852 wrote:Hello guys, I have an issue with my multiplayer game in Java. So it's a turn base board game, I have finished the game logic, I have created a GUI client side, a Server class and a Client class that can connect to the Server. It does multithreading so multiple client can connect, and I can send info to the server. ![[image loading]](http://i.imgur.com/AlJXz2s.png) As you can see, I can connect, and when I click on a case, it sends coordinate. Now my issue is : how the heck do I link the game for all of that to works ? I have the Board class that does all the board modification like flipping pawn, checking valid move etc but I'm lost on this step. So, from what i understand, you already have clients talking to server, and you already have a class with all game logic done. You can can't do the final step of putting those things together. First you must decide what kinda of server you have, does the server have all game information, or does it simply transport client calls? Since it is a board game, and if your task doesn't care about cheating, you server could simply route the messages from one client to another (assuming it is a turn based board game with no time related stuff). Like a chat server. You have all clients with all game logic, your client sends his action to the server and the server routes it to the other client. If you care about cheating or your game deals with real time stuff, you must have all game logic on server.
Yeah, what I want to do :
Client1 and Client2 connect to the Server, Server create the Game, Send Client1 and Client2 an initial Board.
Then Client1 send coordinate to the Server, the Server handle the data, modify the board and send it back to both Clients, then it's Client2 turn etc...
My issue is that I don't know how or where to create the "GameController" instance, and how to put each Client as a Player on the GameController instance.
|
On December 14 2015 05:38 Faust852 wrote:Show nested quote +On December 14 2015 04:58 TMG26 wrote:On December 14 2015 01:06 Faust852 wrote:Hello guys, I have an issue with my multiplayer game in Java. So it's a turn base board game, I have finished the game logic, I have created a GUI client side, a Server class and a Client class that can connect to the Server. It does multithreading so multiple client can connect, and I can send info to the server. ![[image loading]](http://i.imgur.com/AlJXz2s.png) As you can see, I can connect, and when I click on a case, it sends coordinate. Now my issue is : how the heck do I link the game for all of that to works ? I have the Board class that does all the board modification like flipping pawn, checking valid move etc but I'm lost on this step. So, from what i understand, you already have clients talking to server, and you already have a class with all game logic done. You can can't do the final step of putting those things together. First you must decide what kinda of server you have, does the server have all game information, or does it simply transport client calls? Since it is a board game, and if your task doesn't care about cheating, you server could simply route the messages from one client to another (assuming it is a turn based board game with no time related stuff). Like a chat server. You have all clients with all game logic, your client sends his action to the server and the server routes it to the other client. If you care about cheating or your game deals with real time stuff, you must have all game logic on server. Yeah, what I want to do : Client1 and Client2 connect to the Server, Server create the Game, Send Client1 and Client2 an initial Board. Then Client1 send coordinate to the Server, the Server handle the data, modify the board and send it back to both Clients, then it's Client2 turn etc... My issue is that I don't know how or where to create the "GameController" instance, and how to put each Client as a Player on the GameController instance.
The rough outline of what you are looking for:
Controllers handle input, that means you need to have two different GameControllers. One "GameController" on the clients that translates user input into client model changes and one on the server that translates network input into server model changes.
The client game model sends the change request to the server where the server game controller receives and interprets the update information, updates the server game model and then sends the updated game state to both clients. The network clients/sockets should be in a separate "ServerModel" and not part of the controller. The game model only tells the server model the new game state and the server model sends the data to all the clients it knows about.
On the clients, an "UpdateController" receives the new game states and updates the client game model, which then results in a change of the game board - usually using an observer pattern where the user interface is an observer listening for changes in the model and the model sending a change notification to all observers when ever it gets changed.
The tricky part in all that is the second client that doesn't know when the first client does it's move, so it needs to constantly listen to the server and wait until it sends a new game state. Essentially, sending and receiving from the server needs to be completely separate so that you can receive the game state at any point in time. This allows you to have a single point that does the receiving of new game states - and other data (e.g. chat) -, no matter whether it's caused by the action of the current or the other player.
|
Anyone with experience with bugzilla module for python? Like the name suggest it is used to communicate with Bugzilla. I am getting this error:
xmlrpc.client.Fault: <Fault 53: 'query_format is not a valid parameter for the Bugzilla::Bug::match function.'>
(On top of many others but this seems to be main cause.
The thing is i am using query constructor from same module. So i am pretty sure the whole query is constructed in the right way.
Using ubuntu, python3.4, tried 1.0.0 , 1.1.0, and 1.2.2 builds of python-bugzilla.
|
On December 14 2015 03:58 Ropid wrote:
The naming scheme with the eth0, eth1, eth2, ... was about the order of the devices being created at boot and later when you hot-plug something or start another driver module.
The new naming scheme has fixed names that are about the spot where things are connected. The system can now do things like start up devices in parallel and no matter which one is faster, the names will stay the same [EDIT: that was probably a stupid thought. I bet it's more about just being able to start up any device that can be found automatically without having any manual configuration and still be able to count on names staying fixed.]
That "eno1" you see is set up by the BIOS of your machine. For me it's "enp6s0", which is perhaps something about the specific PCI-E lane of the chipset it's connected to.
The BIOS definitely does not assign names to devices such as network cards. The Linux kernel does this at boot time through communicating with udevd, and it bases the name off of BIOS data and/or physical characteristics from the device such as the bus, slot, and MAC address.
You're right about how the traditional naming scheme of ethN, wlanN, etc. worked though. You couldn't rely on device names if you had multiple devices with the same function connected to the system because udev name assignment wasn't always in the same order. The same issue occurred pretty often with hdds. To make this naming method work, you would have to create manual udev rules in /etc/udev/rules.d/ for assigning names based on vendor/manufacturer information and hardware device IDs.
|
On December 15 2015 01:17 suid wrote:Show nested quote +On December 14 2015 03:58 Ropid wrote:
The naming scheme with the eth0, eth1, eth2, ... was about the order of the devices being created at boot and later when you hot-plug something or start another driver module.
The new naming scheme has fixed names that are about the spot where things are connected. The system can now do things like start up devices in parallel and no matter which one is faster, the names will stay the same [EDIT: that was probably a stupid thought. I bet it's more about just being able to start up any device that can be found automatically without having any manual configuration and still be able to count on names staying fixed.]
That "eno1" you see is set up by the BIOS of your machine. For me it's "enp6s0", which is perhaps something about the specific PCI-E lane of the chipset it's connected to. The BIOS definitely does not assign names to devices such as network cards. The Linux kernel does this at boot time through communicating with udevd, and it bases the name off of BIOS data and/or physical characteristics from the device such as the bus, slot, and MAC address. You're right about how the traditional naming scheme of ethN, wlanN, etc. worked though. You couldn't rely on device names if you had multiple devices with the same function connected to the system because udev name assignment wasn't always in the same order. The same issue occurred pretty often with hdds. To make this naming method work, you would have to create manual udev rules in /etc/udev/rules.d/ for assigning names based on vendor/manufacturer information and hardware device IDs.
I meant that "it bases the name off of BIOS data" you mentioned. It seemed to me the "eno..." names can be configured by the guy doing the firmware as opposed to the "enp..." names. I thought when I see that "enp6s0" name here for me, this is because no one working on the board set up anything for it, but they could have also given it a name like "eno1" if they had wanted to.
|
Is there any reason why QT allocates main window on heap? Polymorphism? Does it also use heap for controls?
|
I've heard that complaint a lot, but never really questioned it. My first GUI usage was with GTK and wxWidgets, and I've always allocated windows and view objects on the heap. When we first encountered GUIs in class, allocating stuff on the heap absolutely destroyed my classmates for some reason, while it was quite easy in my opinion. Not really sure why exactly it's necessary, but I don't see it as much as a problem as some of them did (there was a lot of complaining). I'm not sure why but it feels more natural to allocate the views explicitly one at a time versus whenever the constructor decides to.
Apparently all views in Qt are pimpl'd to private views that allocate on the heap anyways so you can't avoid it even if you try.
|
On December 15 2015 07:20 Ropid wrote:Show nested quote +On December 15 2015 01:17 suid wrote:On December 14 2015 03:58 Ropid wrote:
The naming scheme with the eth0, eth1, eth2, ... was about the order of the devices being created at boot and later when you hot-plug something or start another driver module.
The new naming scheme has fixed names that are about the spot where things are connected. The system can now do things like start up devices in parallel and no matter which one is faster, the names will stay the same [EDIT: that was probably a stupid thought. I bet it's more about just being able to start up any device that can be found automatically without having any manual configuration and still be able to count on names staying fixed.]
That "eno1" you see is set up by the BIOS of your machine. For me it's "enp6s0", which is perhaps something about the specific PCI-E lane of the chipset it's connected to. The BIOS definitely does not assign names to devices such as network cards. The Linux kernel does this at boot time through communicating with udevd, and it bases the name off of BIOS data and/or physical characteristics from the device such as the bus, slot, and MAC address. You're right about how the traditional naming scheme of ethN, wlanN, etc. worked though. You couldn't rely on device names if you had multiple devices with the same function connected to the system because udev name assignment wasn't always in the same order. The same issue occurred pretty often with hdds. To make this naming method work, you would have to create manual udev rules in /etc/udev/rules.d/ for assigning names based on vendor/manufacturer information and hardware device IDs. I meant that "it bases the name off of BIOS data" you mentioned. It seemed to me the "eno..." names can be configured by the guy doing the firmware as opposed to the "enp..." names. I thought when I see that "enp6s0" name here for me, this is because no one working on the board set up anything for it, but they could have also given it a name like "eno1" if they had wanted to.
The names are not created by the BIOS or firmware at all.
Udev names the block device nodes that you see in the virtual tmpfs filesystem mounted at /dev, which includes those network interfaces. Udev does not communicate with firmware like you are thinking; there's no support for that. Udev runs in userspace anyway. The kernel talks to the firmware and raises events to udev as drivers are loaded. Udev then matches these events with Udev rules for naming the device. You alter the way the devices are named through these rules, the firmware developer doesn't. Why would they even care how their device is named by the Linux kernel/Udev anyway?
|
On December 15 2015 09:35 suid wrote:Show nested quote +On December 15 2015 07:20 Ropid wrote:On December 15 2015 01:17 suid wrote:On December 14 2015 03:58 Ropid wrote:
The naming scheme with the eth0, eth1, eth2, ... was about the order of the devices being created at boot and later when you hot-plug something or start another driver module.
The new naming scheme has fixed names that are about the spot where things are connected. The system can now do things like start up devices in parallel and no matter which one is faster, the names will stay the same [EDIT: that was probably a stupid thought. I bet it's more about just being able to start up any device that can be found automatically without having any manual configuration and still be able to count on names staying fixed.]
That "eno1" you see is set up by the BIOS of your machine. For me it's "enp6s0", which is perhaps something about the specific PCI-E lane of the chipset it's connected to. The BIOS definitely does not assign names to devices such as network cards. The Linux kernel does this at boot time through communicating with udevd, and it bases the name off of BIOS data and/or physical characteristics from the device such as the bus, slot, and MAC address. You're right about how the traditional naming scheme of ethN, wlanN, etc. worked though. You couldn't rely on device names if you had multiple devices with the same function connected to the system because udev name assignment wasn't always in the same order. The same issue occurred pretty often with hdds. To make this naming method work, you would have to create manual udev rules in /etc/udev/rules.d/ for assigning names based on vendor/manufacturer information and hardware device IDs. I meant that "it bases the name off of BIOS data" you mentioned. It seemed to me the "eno..." names can be configured by the guy doing the firmware as opposed to the "enp..." names. I thought when I see that "enp6s0" name here for me, this is because no one working on the board set up anything for it, but they could have also given it a name like "eno1" if they had wanted to. The names are not created by the BIOS or firmware at all. Udev names the block device nodes that you see in the virtual tmpfs filesystem mounted at /dev, which includes those network interfaces. Udev does not communicate with firmware like you are thinking; there's no support for that. Udev runs in userspace anyway. The kernel talks to the firmware and raises events to udev as drivers are loaded. Udev then matches these events with Udev rules for naming the device. You alter the way the devices are named through these rules, the firmware developer doesn't. Why would they even care how their device is named by the Linux kernel/Udev anyway?
They can just set the number, that "1" in "eno1". It could be neat for their documentation. Like, they could promise that the Intel LAN they've put on the board will show up as number 1 and a third party controller as number 2, or when they build a board with four hot-plug capable slots on it, they can promise that what you plug into the first slot will show up as "ens1", second will be "ens2", etc.
|
On December 15 2015 10:13 Ropid wrote:Show nested quote +On December 15 2015 09:35 suid wrote:On December 15 2015 07:20 Ropid wrote:On December 15 2015 01:17 suid wrote:On December 14 2015 03:58 Ropid wrote:
The naming scheme with the eth0, eth1, eth2, ... was about the order of the devices being created at boot and later when you hot-plug something or start another driver module.
The new naming scheme has fixed names that are about the spot where things are connected. The system can now do things like start up devices in parallel and no matter which one is faster, the names will stay the same [EDIT: that was probably a stupid thought. I bet it's more about just being able to start up any device that can be found automatically without having any manual configuration and still be able to count on names staying fixed.]
That "eno1" you see is set up by the BIOS of your machine. For me it's "enp6s0", which is perhaps something about the specific PCI-E lane of the chipset it's connected to. The BIOS definitely does not assign names to devices such as network cards. The Linux kernel does this at boot time through communicating with udevd, and it bases the name off of BIOS data and/or physical characteristics from the device such as the bus, slot, and MAC address. You're right about how the traditional naming scheme of ethN, wlanN, etc. worked though. You couldn't rely on device names if you had multiple devices with the same function connected to the system because udev name assignment wasn't always in the same order. The same issue occurred pretty often with hdds. To make this naming method work, you would have to create manual udev rules in /etc/udev/rules.d/ for assigning names based on vendor/manufacturer information and hardware device IDs. I meant that "it bases the name off of BIOS data" you mentioned. It seemed to me the "eno..." names can be configured by the guy doing the firmware as opposed to the "enp..." names. I thought when I see that "enp6s0" name here for me, this is because no one working on the board set up anything for it, but they could have also given it a name like "eno1" if they had wanted to. The names are not created by the BIOS or firmware at all. Udev names the block device nodes that you see in the virtual tmpfs filesystem mounted at /dev, which includes those network interfaces. Udev does not communicate with firmware like you are thinking; there's no support for that. Udev runs in userspace anyway. The kernel talks to the firmware and raises events to udev as drivers are loaded. Udev then matches these events with Udev rules for naming the device. You alter the way the devices are named through these rules, the firmware developer doesn't. Why would they even care how their device is named by the Linux kernel/Udev anyway? They can just set the number, that "1" in "eno1". It could be neat for their documentation. Like, they could promise that the Intel LAN they've put on the board will show up as number 1 and a third party controller as number 2, or when they build a board with four hot-plug capable slots on it, they can promise that what you plug into the first slot will show up as "ens1", second will be "ens2", etc.
Oh, you're just making up ideas now.
|
If you had to create a weighted chooser in as few lines of code as possible, while still being easily changeable, how would you do so?
For example, i=randint()
if (i<0.1):
blah
elseif (i<0.2):
blah2
etc.
is out because if you change any weight you have to change them all. What're your ideas?
|
On December 15 2015 12:02 suid wrote:Show nested quote +On December 15 2015 10:13 Ropid wrote:On December 15 2015 09:35 suid wrote:On December 15 2015 07:20 Ropid wrote:On December 15 2015 01:17 suid wrote:On December 14 2015 03:58 Ropid wrote:
The naming scheme with the eth0, eth1, eth2, ... was about the order of the devices being created at boot and later when you hot-plug something or start another driver module.
The new naming scheme has fixed names that are about the spot where things are connected. The system can now do things like start up devices in parallel and no matter which one is faster, the names will stay the same [EDIT: that was probably a stupid thought. I bet it's more about just being able to start up any device that can be found automatically without having any manual configuration and still be able to count on names staying fixed.]
That "eno1" you see is set up by the BIOS of your machine. For me it's "enp6s0", which is perhaps something about the specific PCI-E lane of the chipset it's connected to. The BIOS definitely does not assign names to devices such as network cards. The Linux kernel does this at boot time through communicating with udevd, and it bases the name off of BIOS data and/or physical characteristics from the device such as the bus, slot, and MAC address. You're right about how the traditional naming scheme of ethN, wlanN, etc. worked though. You couldn't rely on device names if you had multiple devices with the same function connected to the system because udev name assignment wasn't always in the same order. The same issue occurred pretty often with hdds. To make this naming method work, you would have to create manual udev rules in /etc/udev/rules.d/ for assigning names based on vendor/manufacturer information and hardware device IDs. I meant that "it bases the name off of BIOS data" you mentioned. It seemed to me the "eno..." names can be configured by the guy doing the firmware as opposed to the "enp..." names. I thought when I see that "enp6s0" name here for me, this is because no one working on the board set up anything for it, but they could have also given it a name like "eno1" if they had wanted to. The names are not created by the BIOS or firmware at all. Udev names the block device nodes that you see in the virtual tmpfs filesystem mounted at /dev, which includes those network interfaces. Udev does not communicate with firmware like you are thinking; there's no support for that. Udev runs in userspace anyway. The kernel talks to the firmware and raises events to udev as drivers are loaded. Udev then matches these events with Udev rules for naming the device. You alter the way the devices are named through these rules, the firmware developer doesn't. Why would they even care how their device is named by the Linux kernel/Udev anyway? They can just set the number, that "1" in "eno1". It could be neat for their documentation. Like, they could promise that the Intel LAN they've put on the board will show up as number 1 and a third party controller as number 2, or when they build a board with four hot-plug capable slots on it, they can promise that what you plug into the first slot will show up as "ens1", second will be "ens2", etc. Oh, you're just making up ideas now.
Yeah, I don't know the details about what's going on. I'm only guessing from that marketing blurb about this scheme that the systemd guys have here:
http://www.freedesktop.org/wiki/Software/systemd/PredictableNetworkInterfaceNames/
They write this:
"The following different naming schemes for network interfaces are now supported by udev natively:
- Names incorporating Firmware/BIOS provided index numbers for on-board devices (example: eno1)
- Names incorporating Firmware/BIOS provided PCI Express hotplug slot index numbers (example: ens1)
- Names incorporating physical/geographical location of the connector of the hardware (example: enp2s0)
- Names incorporating the interfaces's MAC address (example: enx78e7d1ea46da)
- Classic, unpredictable kernel-native ethX naming (example: eth0)"
That's where I got the idea. I thought those numbers were set by someone working on the BIOS.
|
|
|
|
|
|
![[image loading]](http://i.imgur.com/AlJXz2s.png)